Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities suchGreenhouse effect Quick Reference The trapping of the sun's warmth in a planet's lower atmosphere due to the greater transparency of the atmosphere to visible radiation from the sun than to infrared radiation emitted from the planet's surfaceGreenhouse Effect Teaching Box This teaching box provides resources related to the greenhouse effect It will help you teach how the greenhouse effect works, and how it prevents Earth from becoming a frozen ball of ice!

The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
Greenhouse effect definition science
Greenhouse effect definition science-Greenhouse effect definition, an atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by shortwave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longerwavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases;Greenhouse effect is being strengthened as human activities (such as the combustion of fossil fuels) add more of these gases to the atmosphere, resulting in a shift in the Earth's equilibrium Climate Change Science Facts Climate change is a real and urgent challenge that is already affecting people and the environment worldwide




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
The greenhouse effect, in turn, is one of the leading causes of global warming The most significant greenhouse gases, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), are water vapor (H2OGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on EarthDefinition of Greenhouse effect The effect produced as greenhouse gases allow incoming solar radiation to pass through the Earth's atmosphere, but prevent part of the outgoing infrared radiation from the Earth's surface and lower atmosphere from escaping into outer space
The Science of Global warmingthe Greenhouse condition is over 100 years old and is not 'exotic' but basic science The science is solid and basic physics The doubt comes from what some believe is the human imprint to warming which actually has been very strong increased industrialization shows the burning of fossil fuels to haveToo Cool for School Curriculum Gridnavigate by day or discipline You are in the Science discipline DAY 1 Goal To understand the definition, types and origins of the major greenhouse gases Objective Students will Create a town with all the elements to sustain human life Discuss how the activities of the people in the town may createThis is a PDFonly article The first page of the PDF of this article appears
A greenhouse is for growing plants It is made of glass or clear plastic to let in lots of sunlight But why not just put the plants outside?The greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere , the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now That would make it too cold to support life as we know itCaused by atmospheric gases that allow sunshine to pass through but absorb heat that is radiated back from the warmed surface of the earth



1




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
The greenhouse effect, explained The basic explanation for why CO2 and other greenhouse gases warm the planet is so simple and has been known science for more than aThe most important greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide(CO 2), and Greenhouse effect definition The greenhouse effect is the problem caused by increased quantities of gases such as Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gasesThe atmospheric gases and a greenhouse work in quite different ways, but the resulting effect, higher temperature in both cases, has led to the nomenclature "greenhouse gases" for the atmospheric gases responsible for the atmospheric warming effect Although this nomenclature is misleading, it is in such common use that we use it here as wellThe greenhouse effect occurs when certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere (the air around the Earth) trap infrared radiationThis makes the planet become warmer, similar to the way it makes a greenhouse become warmer The greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases;




Climate Change Science Atmospheric Balance Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World




The Greenhouse Effect Explained
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxidesThus, the rising level of "Greenhouse Effect" Definition By ROGER W PEASE JR See all Hide authors and affiliations Science Vol 191, Issue 4223, pp 138 DOI /science Article;




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education




Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known asThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methaneA greenhouse stays warmer than the air outside Instead of cooling off at night, it traps some of the heat inside to




The Greenhouse Effect And Causes Of Climate Change




Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
Science and Tech Educators The Greenhouse Effect Life in a greenhouse? The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface The greenhouse effect happens when these gases gather in the Earth's atmosphere According to scientists, without the greenhouse effect, the average temperature of the Earth would drop from 57 degrees Fahrenheit (14 degrees Celsius) to as low as negative 04 degrees F (minus 18 degrees C) Do We Blame the Industrial Revolution?



Environment For Kids Global Warming
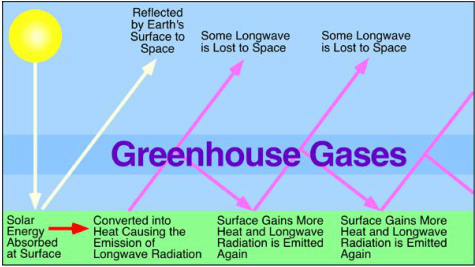



Ess Topic 6 1 Introduction To The Atmosphere Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
Describes how greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor, trap heat in the atmosphere, and that levels of these gases are increasing due to human activities Concept Map Discover related concepts in Math and Science CK12 Content Community ContentThe greenhouse effect is the process in which the emission of infrared radiation by the atmosphere warms a planet's surface The name comes from an analogy with the warming of Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect and climate change Effects of climatic change Resources The greenhouse effect is the retention by Earth ' s atmosphere in the form of heat some of the energy that arrives from the sun as light Certain gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), are transparent to most of the wavelengths




Global Warming Potential Definition And Examples




Difference Between Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Define greenhouse effects greenhouse effects synonyms, greenhouse effects pronunciation, greenhouse effects translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse effects greenhouse effect Energy radiated by the sun converts to heat when it reaches the earthGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
Science Vol 191, Issue 4223, pp 138 DOI /scienceLearn about the greenhouse effect and get great science fair experiment ideas Read moreGreenhouse gas definition is any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect How to use greenhouse gas in a sentence




Human Influence On The Greenhouse Effect Globalchange Gov



Carbon Cycle And The Earth S Climate
The Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon in which the specific gases in the atmosphere of the Earth trap heat from the sun (see The Greenhouse Effect Diagram attachment) Typically, our atmosphere absorbs just the right amount of heat so that living things can surviveThe greenhouse effect Some electromagnetic radiation from the Sun passes through Earth's atmosphere This includes infrared radiation , visible light and ultraviolet radiation Greenhouse effect definition is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to



The Greenhouse Effect And The 2nd Law Of Thermodynamics



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
Greenhouse effect warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere;Greenhouse Earth Overview A "greenhouse Earth" is a period during which no continental glaciers exist anywhere on the planet Additionally, the levels of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases (such as water vapor and methane) are high, and sea surface temperatures (SSTs) range from 28 °C (4 °F) in the tropics to 0 °C (32 °F) in the polar regionsTeaching Boxes are collections of classroomready and standardsaligned activities, content, and multimedia that build
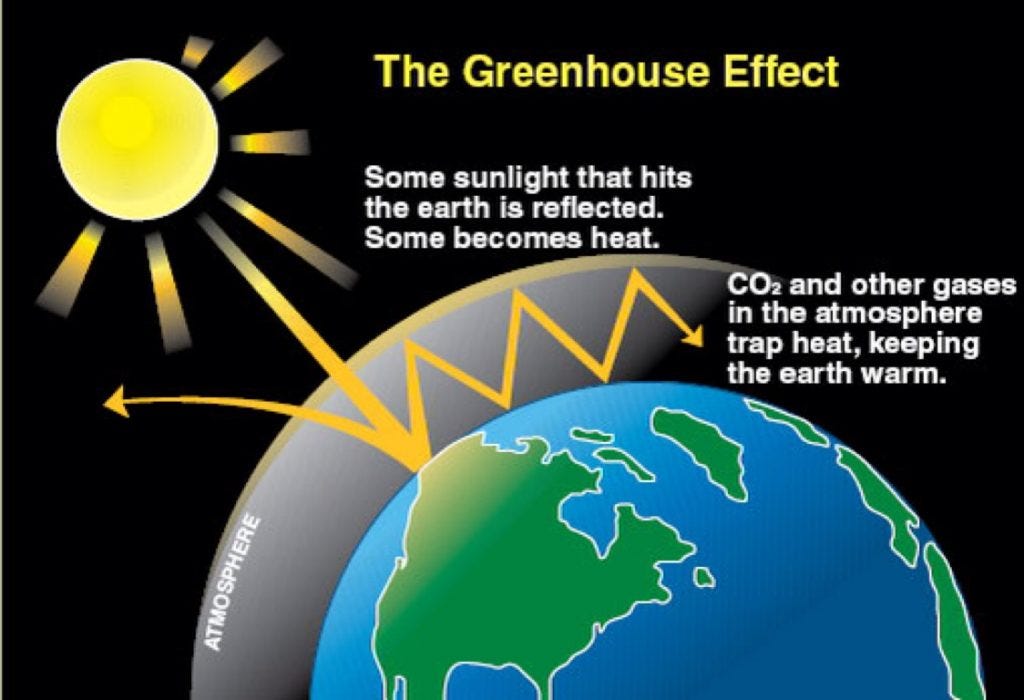



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
The greenhouse effect meaning 1 an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere (= mixture of Learn more
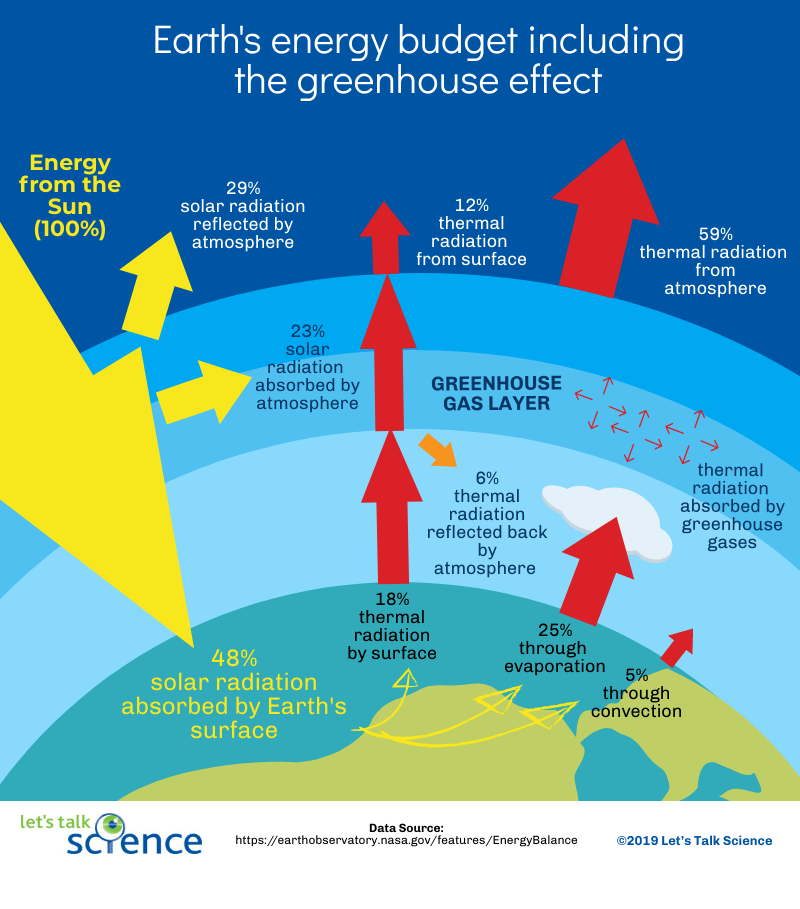



What Is Ocean Warming And Why Does It Matter Let S Talk Science



Greenhouse Effect Lincoln University
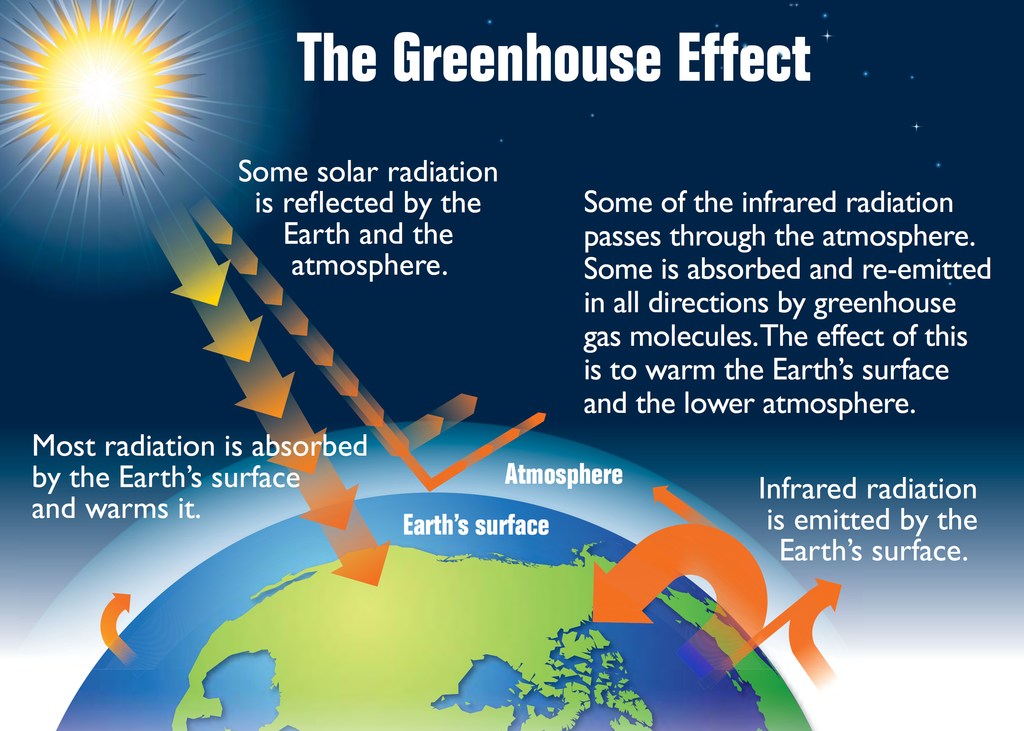



What Is The Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect And Carbon Dioxide Zhong 13 Weather Wiley Online Library




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science



3




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
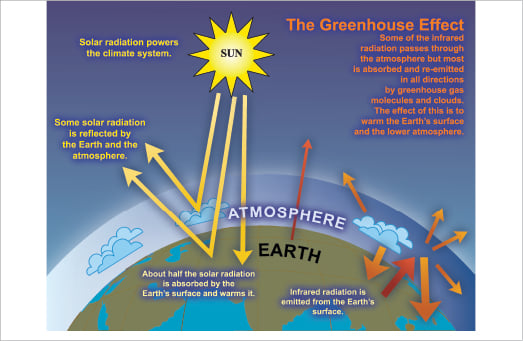



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science
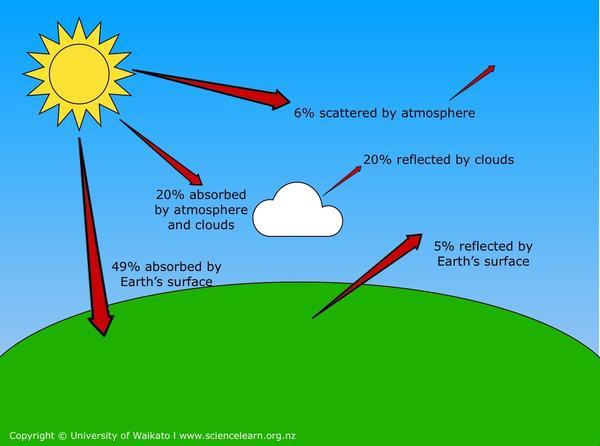



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub




Global Warming Definition And Meaning Market Business News
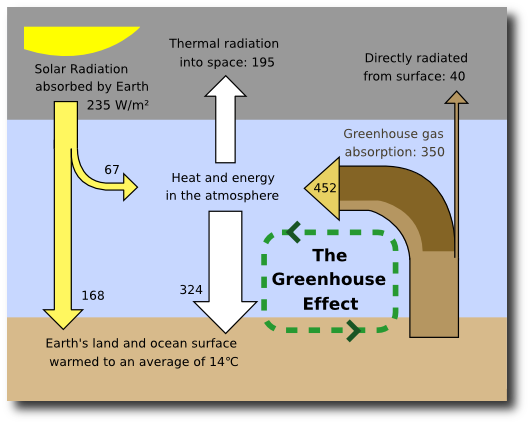



Climate Change And Global Warming Introduction Global Issues




Science Vincent




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
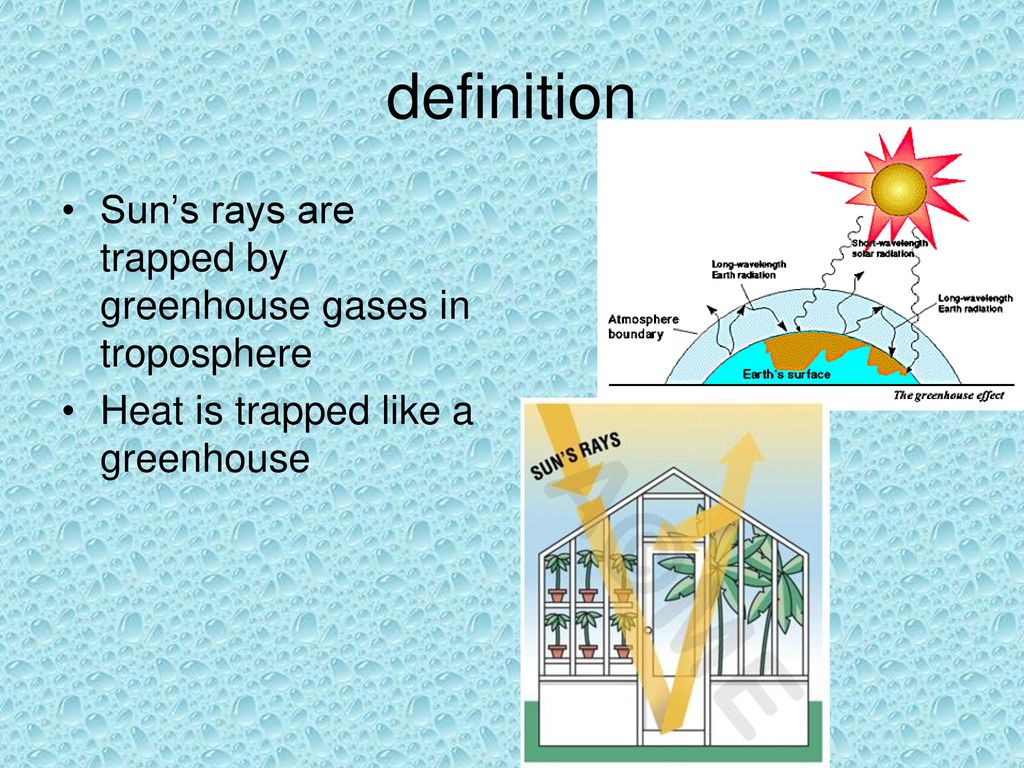



Greenhouse Effect Ppt Download




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



The Greenhouse Effect



Untitled Document




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Earth S Energy Budget Wikipedia



Greenhouse Effect




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Definition Impact Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Green House Effect




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Effect Definition Science




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Ned Nikolov Ph D Did You Know That The Fundamental Definition Of The Greenhouse Effect Via The Absorption Of Outgoing Ir Radiation By The Atmosphere Produces Nonsensical Results Over Antarctica According



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
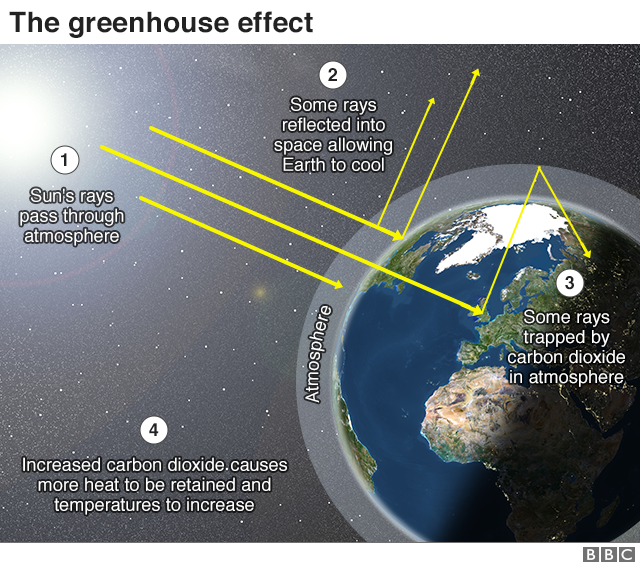



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Definition Solution Facts




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa



Greenhouse Effect Body Used Water Process Earth Plants Form Energy Gas




Greenhouse Effect Video For Kids The Greenhouse Effect Youtube




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education
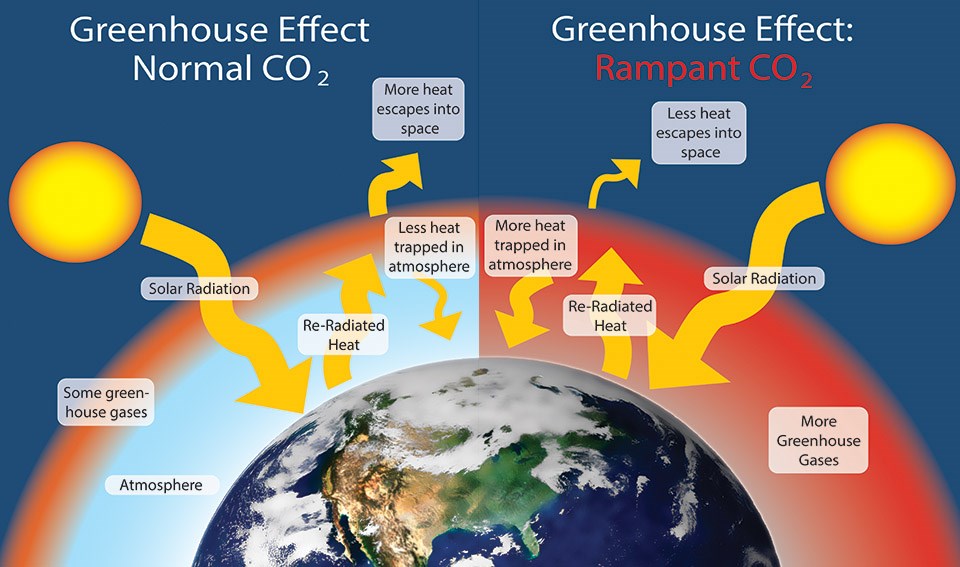



The Physical Basis
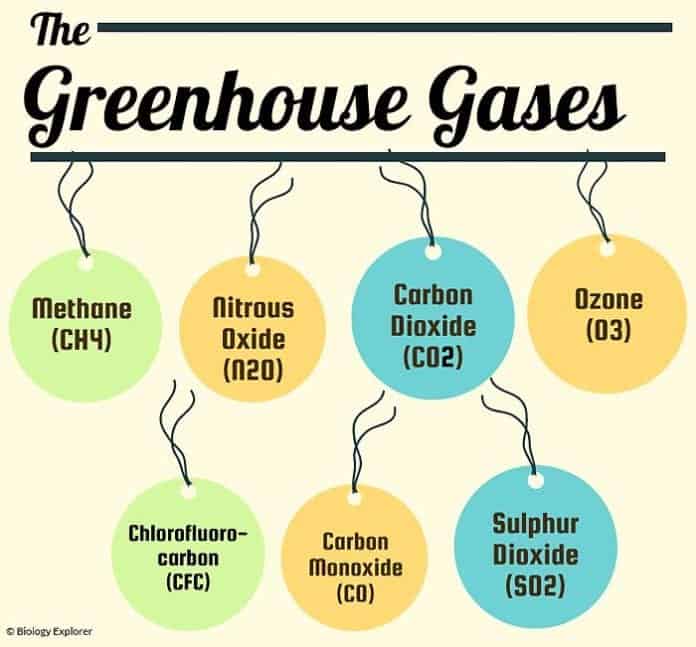



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Ned Nikolov Ph D Do You Know That The Very Definition Of The Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Utilized By Modern Climate Science Makes No Physical Sense Take A Look At These Slides




Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect



Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Definition Geography




Runaway Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect And Gases Tfhs 9th Grade Super Mega Honors Science




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
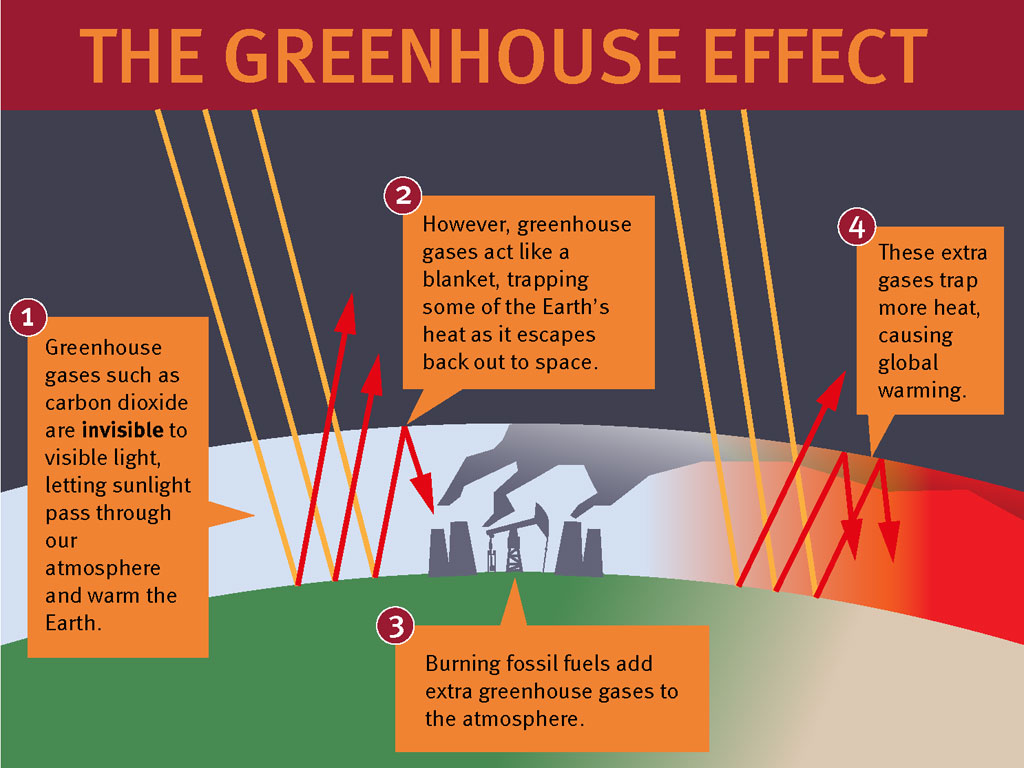



Greenhouse Effect



1




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay
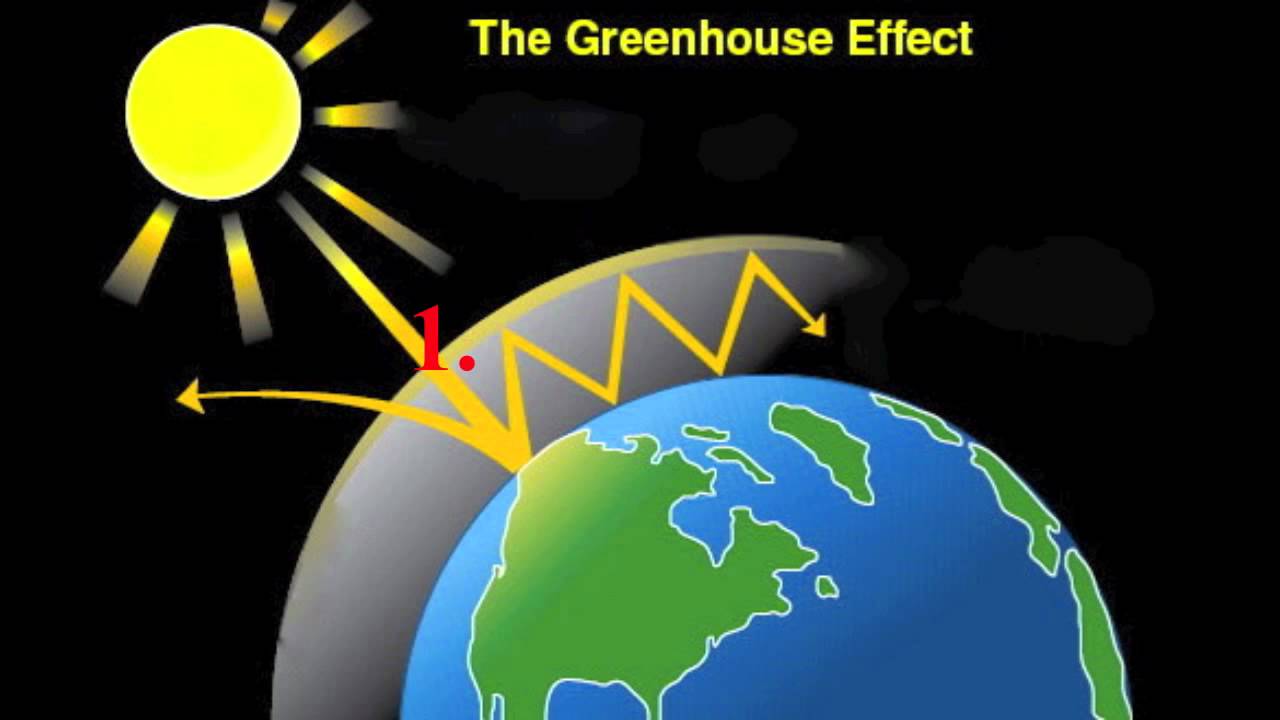



The Greenhouse Effect Youtube




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy
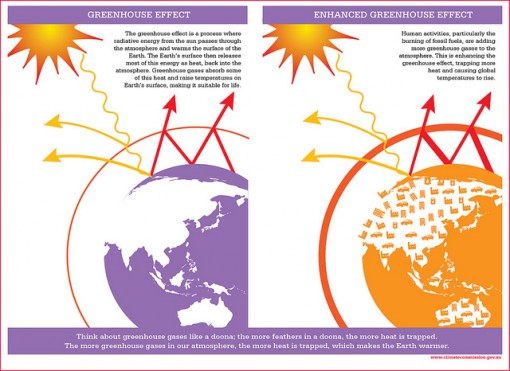



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




Global Warming National Geographic Society




Greenhouse Effect Definition Easy To Understand




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Environment Air Pollution Global Warming Facts Effects Of Global Warming Ozone Layer



1




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube
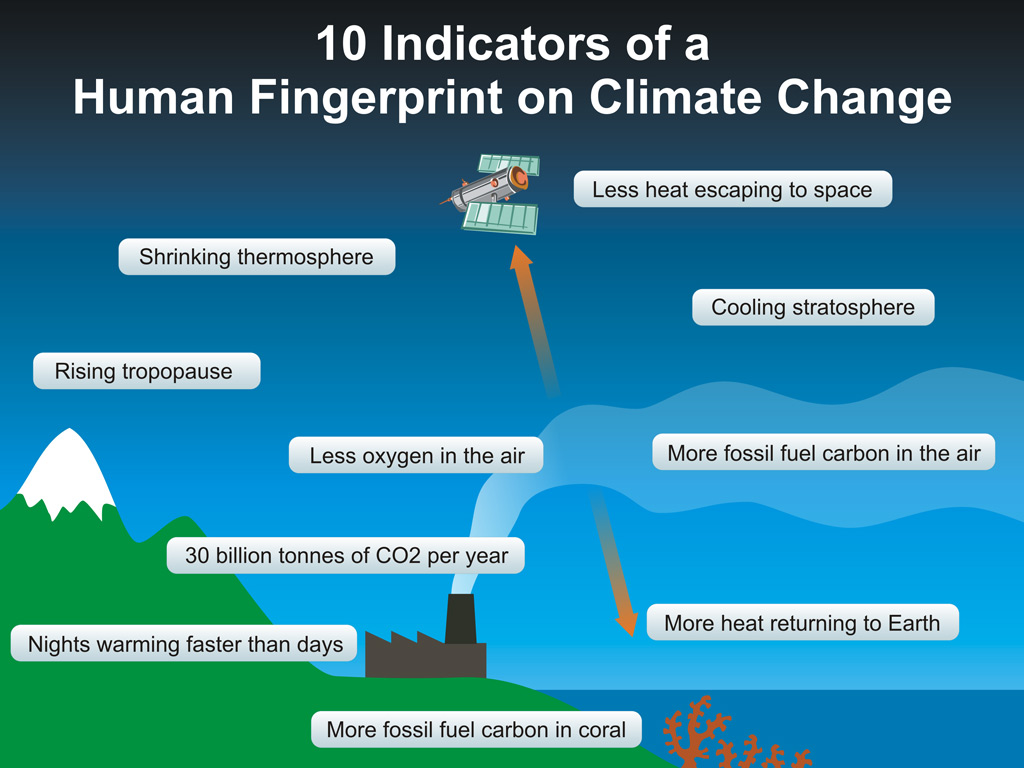



The Human Fingerprint In Global Warming
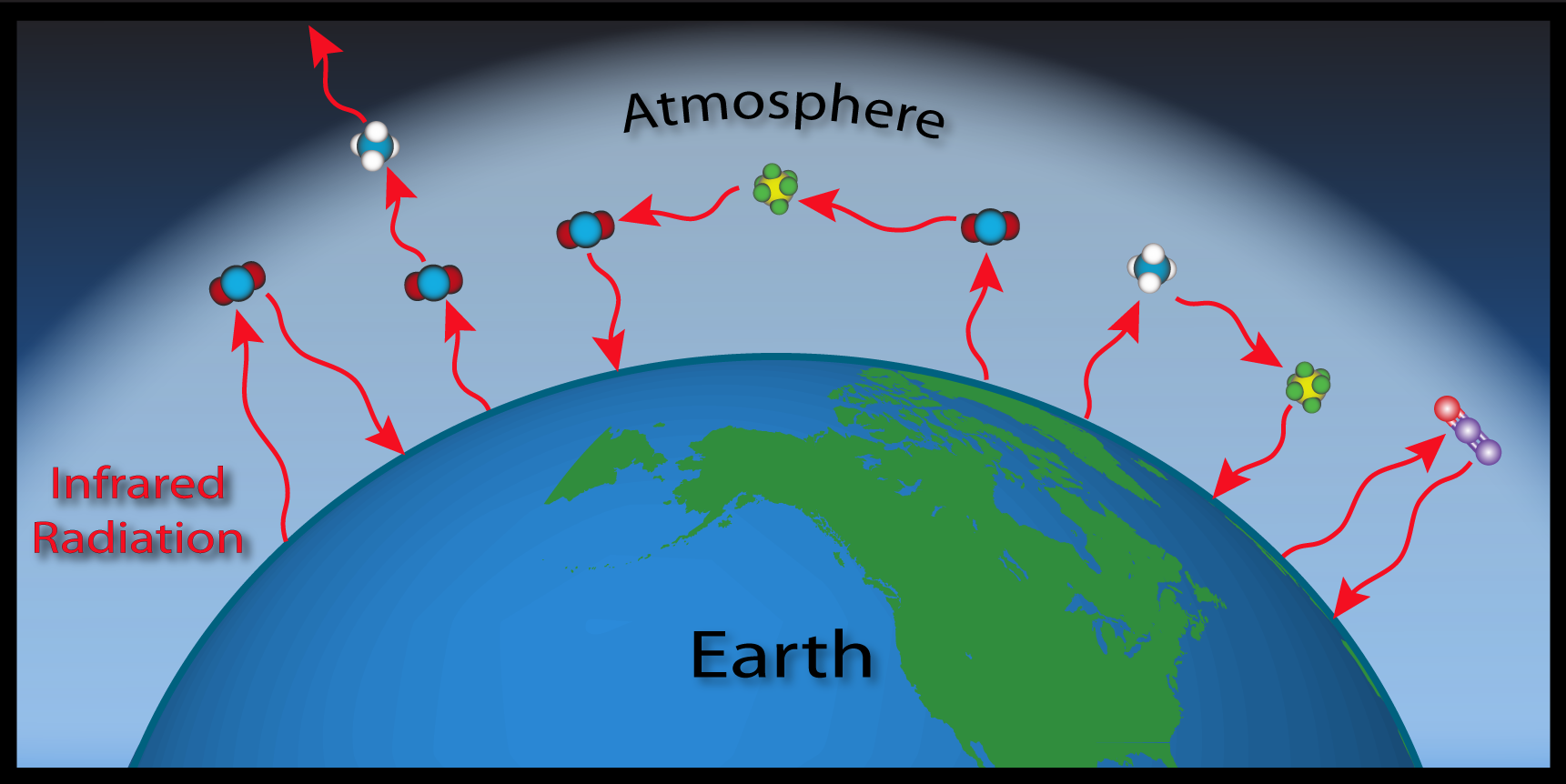



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Sustainable Energy The Future Is Clear We Must Move Forward With Sustainable Energy Green Planet Ethics




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿